|
Clinical
Breast Exam
(CBE) |
|
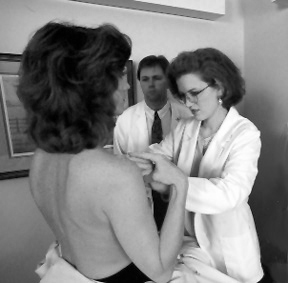 |
General
Approach
|
|
Clinical
Breast Exam
(CBE) |
|
 |
General
Approach
|
|
Patient
Preparation
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
Arms
Over Head
|
||
 |
 |
|
|
Check
For:
|
||
|
Arms
On Hips
|
|
 |
 |
|
Observe
factors that influence breast appearance:
|
|
|
|
|
Bimanual
Compression
|
 |
|
To
Discover Masses Not Palpable In Supine Position
|
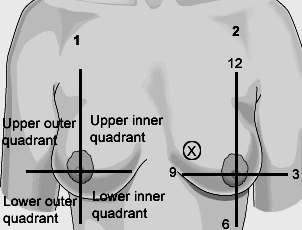
| Documentation | |
|
|
|
Two methods may be used for the documentation and description of the breast. 1. The breast may be divided into 4 quadrants - upper and lower outer quadrants and upper and lower inner quadrants. 2. The breast is described in reference to the face of a clock. A mass or finding maybe located by the quadrant or by the "time and distance from the nipple. Example: 2-3 cm stony mass, palpated 4 cm from the nipple at the 10 o'clock position |
|
Nipple
Compression
|
|
 |
|
|
Check
For Discharge
|
|
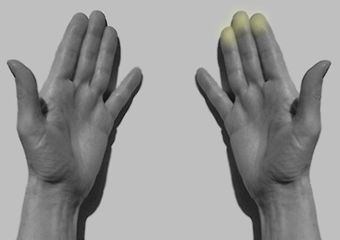
Basic
Hand Technique
|
 |
|
|
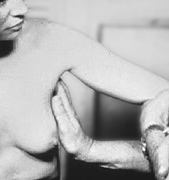
Lymph
Node Palpation
|
|
 |
 |
|
Explain The Procedure
|
|
|
Lymph
Node Palpation
|
|
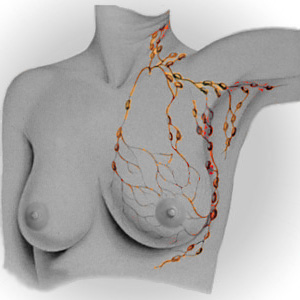 |
Check
|
|
|
|
Breast
Tissue Examination
|
|
 |
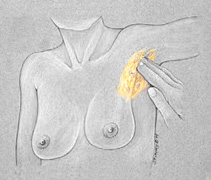
Palpate
|
Remember: The consistency of breast tissue varies with age. |
|
|
Breast
Palpation
|
|
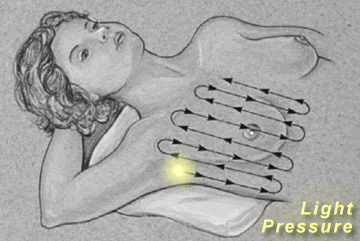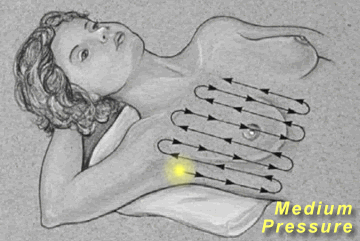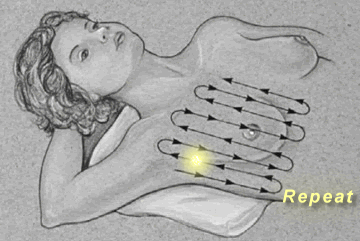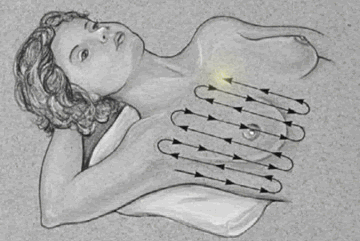 |
Palpate
|
|
|
|
Male
Breast Tissue
|
|
 |
1400
men per year Commonly presents as:
|
|
|
| Examination of the male breast should not be omitted. The underdeveloped breast tissue in some men may be palpated as a firm button of tissue 2 cm or more in diameter. This thin disc is covered by a small nipple and aerola. Perform a visual inspection and palpate the areola and nipple for masses, nodules, swelling and ulceration. Men do not need to have mammograms. | |
|
Key
Points to Remember
|
|